FHA loans are government-backed mortgages insured by the Federal Housing Administration (FHA), which was established in 1934 to help stabilize the housing market during the Great Depression. The FHA does not lend money directly; instead, it insures loans made by approved lenders. This insurance reduces the lenders risk, making it easier for borrowers to qualify for a loan, especially those with lower credit scores or limited savings for a down payment.
FHA loans allow borrowers to secure a mortgage with a down payment as low as 3.5% if they have a credit score of at least 580. Borrowers with credit scores between 500 and 579 may still qualify, but they will need to make a 10% down payment. FHA loans are available for various property types, including single-family homes and multi-unit properties, but the home must be the borrowers primary residence. FHA loans also come with mandatory mortgage insurance premiums (MIP), which include an upfront cost of 1.75% of the loan amount and annual premiums that vary depending on the loan terms and down payment.
Who qualifies for an FHA loan?
Qualifying for an FHA loan is generally easier than for a conventional mortgage, making it an attractive option for first-time homebuyers and those with less-than-perfect credit. To qualify, you must meet the following criteria:
- Credit Score: A minimum credit score of 580 is required to qualify for a 3.5% down payment. If your credit score is between 500 and 579, you can still qualify, but you will need to make a 10% down payment.
- Income and Employment: You must demonstrate a steady income and stable employment history. Your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) should be no more than 43%, though some lenders allow a higher DTI with compensating factors.
- Property Requirements: The home you purchase must be your primary residence, and it must meet certain safety and livability standards. FHA loans cannot be used for investment properties.
What credit score do you need for an FHA loan?
The FHA has relatively lenient credit score requirements compared to conventional loans. To qualify for an FHA loan with the minimum down payment of 3.5%, you need a credit score of at least 580. If your credit score is between 500 and 579, you may still qualify, but you will need to make a 10% down payment.
How much down payment is required for an FHA loan?
The down payment required for an FHA loan largely depends on your credit score. If you have a credit score of 580 or higher, you can qualify for an FHA loan with a down payment as low as 3.5% of the homes purchase price. For example, if you are buying a home for $250,000, you did need to come up with $8,750 for the down payment, if your credit score falls between 500 and 579, you will need to make a higher down payment of at least 10%. In this case, the down payment on the same $250,000 home would be $25,000.
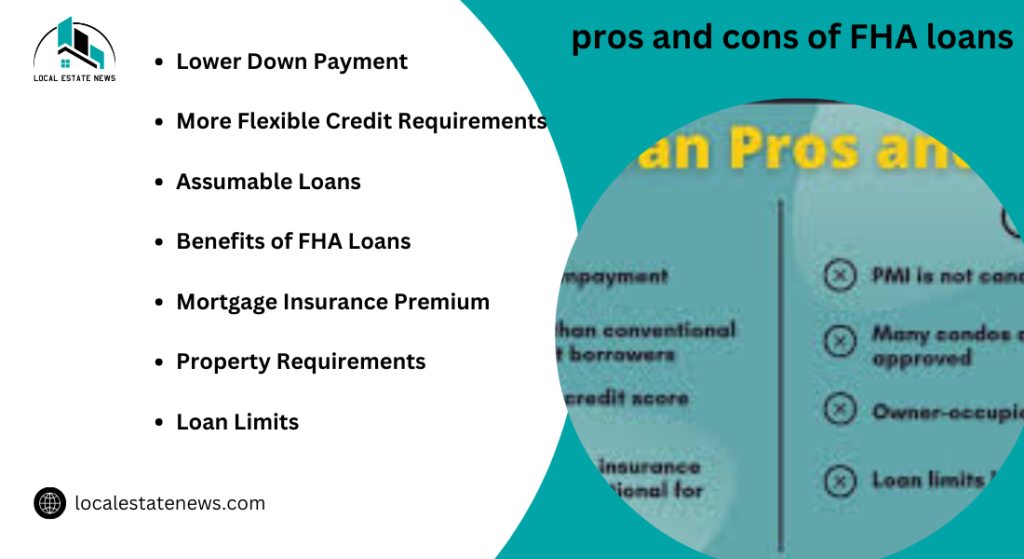
What are the pros and cons of FHA loans?
FHA loans offer several advantages that make them an attractive option for many homebuyers. The primary benefit is the lower down payment requirement, which can be as low as 3.5% for those with a credit score of 580 or above. FHA loans have more lenient credit requirements compared to conventional loans, making homeownership accessible to individuals with lower credit scores. FHA loans also allow the use of gift funds for the down payment, which can ease the financial burden on the buyer.
There are also some drawbacks to consider. The main disadvantages is the requirement to pay mortgage insurance premiums (MIP), both upfront and annually, for the life of the loan. This can increase the overall cost of the loan. Furthermore, FHA loans have loan limits that may not be sufficient in high-cost areas, potentially limiting the types of homes you can purchase with this type of loan. Additionally, FHA loans can only be used for primary residences, so they are not an option for purchasing investment properties.
How does FHA mortgage insurance work?
FHA mortgage insurance is a mandatory part of obtaining an FHA loan, designed to protect the lender in case you default on the loan. There are two components to this insurance: an upfront mortgage insurance premium (UFMIP) and an annual mortgage insurance premium (MIP). The UFMIP is 1.75% of the loan amount, which can be paid at closing or rolled into the loan. For example, on a $250,000 loan, the UFMIP would be $4,375.
The annual MIP varies depending on the loan term, loan amount, and the loan-to-value (LTV) ratio. This premium is divided into monthly payments and added to your mortgage payment. Unlike conventional loans where private mortgage insurance (PMI) can be removed once you reach 20% equity, FHA loans require you to pay MIP for the life of the loan unless you refinance to a conventional loan
What are the FHA loan limits for 2024?
The FHA loan limits for 2024 have been adjusted to reflect the rising home prices across the United States. For single-unit properties, the national “floor” for FHA loans in low-cost areas is set at $498,257. In high-cost areas, the “ceiling” is $1,149,825. These limits are higher in special exception areas like Alaska, Hawaii, Guam, and the U.S. Virgin Islands, where the ceiling for single-unit homes reaches up to $1,724,725. FHA loan limits increase for multi-unit properties, with the maximum limit for four-unit properties reaching up to $2,211,600 in high-cost areas.
How to apply for an FHA loan?
Applying for an FHA loan involves several key steps. First, ensure you meet the basic qualifications, such as having a credit score of at least 580 for a 3.5% down payment or 500 for a 10% down payment. Next, you will need to gather necessary documents, including proof of income, employment history, and credit reports. Afterward, you can apply through an FHA-approved lender who will guide you through the process of getting pre-approved, selecting a loan amount, and ultimately finalizing the loan terms.
What are the different types of FHA loans available?
FHA offers several types of loans to accommodate different homebuyer needs. The most common is the traditional FHA loan, used for purchasing a primary residence. Another option is the FHA 203(k) loan, which combines the mortgage and home renovation costs into a single loan. For seniors, the FHA also offers the Home Equity Conversion Mortgage (HECM), which is a reverse mortgage program, there are specialized loans like the FHA Energy Efficient Mortgage (EEM), which helps homeowners make energy-efficient improvements
How do FHA 203(k) loans work for home renovations?
FHA 203(k) loans are designed to help homebuyers and homeowners finance both the purchase (or refinance) of a house and the cost of its rehabilitation through a single mortgage. There are two main types of FHA 203(k) loans: the Standard 203(k) and the Limited 203(k). The Standard 203(k) is intended for more extensive renovation projects, including structural changes and room additions. This loan requires a HUD-approved consultant to oversee the project. On the other hand, the Limited 203(k) is suited for smaller repairs and improvements, such as updating appliances or replacing a roof, with a maximum renovation budget of $35,000.

Can you refinance with an FHA loan?
Yes, FHA loans offer refinancing options through programs like the FHA Streamline Refinance and the FHA Cash-Out Refinance. The FHA Streamline Refinance is popular because it requires less documentation and has more lenient credit requirements compared to conventional refinancing. It is designed to lower your interest rate or convert an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) to a fixed-rate mortgage, all without needing a new appraisal. The FHA Cash-Out Refinance allows you to tap into your homes equity by replacing your existing mortgage with a new, larger loan, which includes your current balance and the cash amount you want to take out.
How do FHA loans compare to conventional loans?
FHA loans differ from conventional loans in several key areas. FHA loans are insured by the Federal Housing Administration, allowing lenders to offer lower down payments (as low as 3.5%) and more flexible credit requirements (as low as a 580 credit score). In contrast, conventional loans require a higher credit score (at least 620) and a down payment of 5% to 20%. FHA loans require mortgage insurance premiums (MIP) for the life of the loan, while conventional loans allow borrowers to cancel private mortgage insurance (PMI) once they reach 20% equity. FHA loans are generally easier to qualify for, making them a popular choice for first-time homebuyers
What are the closing costs associated with FHA loans?
Closing costs for FHA loans range between 2% to 6% of the loan amount, depending on various factors, the loan size, lender fees, and the state in which the property is located. These costs can include several types of fees, lender fees (origination, processing, and underwriting fees), third-party fees (like appraisal, title insurance, and notary fees), and prepaid expenses (property taxes and homeowners insurance). FHA loans require an upfront mortgage insurance premium (UFMIP) of 1.75% of the loan amount, which can be paid at closing or rolled into the loan.
What are the income requirements for an FHA loan?
To qualify for an FHA loan, borrowers need to demonstrate a steady income and a manageable level of debt relative to their income. While there is no specific minimum income requirement, the FHA looks for a debt-to-income (DTI) ratio of no more than 43%. This means that your monthly debts, including your potential mortgage payment, should not exceed 43% of your gross monthly income, some lenders might allow a higher DTI with compensating factors, a higher credit score or a larger down payment.
What documents are needed to apply for an FHA loan?
When applying for an FHA loan, you will need to provide a range of documents to verify your financial situation. These include recent pay stubs, W-2 forms or tax returns from the past two years, bank statements, and documentation of any other sources of income. you will need to provide information on your debts, credit card statements, auto loans, and any other outstanding loans. If you are receiving gift funds to help with the down payment or closing costs, you will also need a gift letter verifying that the funds are a gift and not a loan
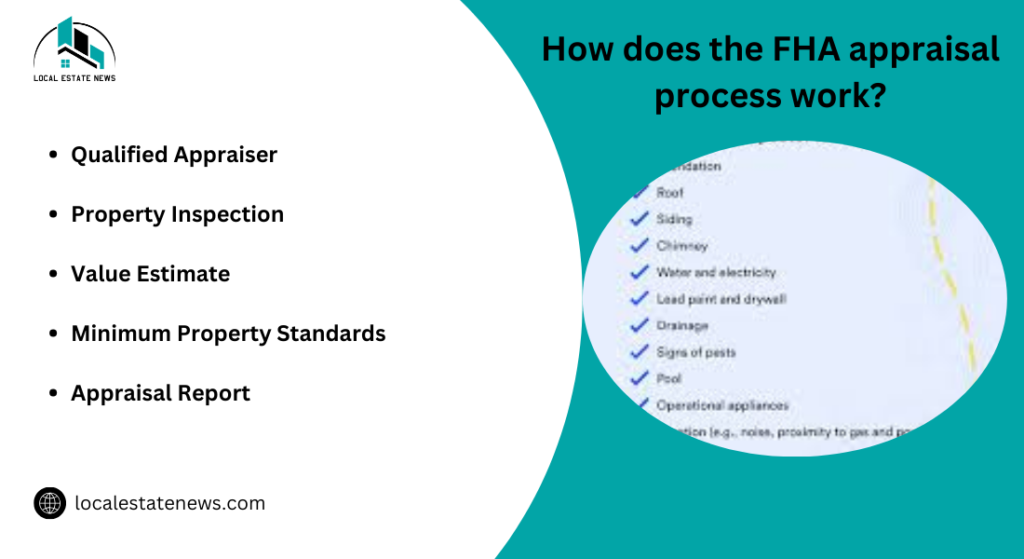
How does the FHA appraisal process work?
The FHA appraisal process serves two main purposes: determining the fair market value of the property and ensuring that the home meets the Federal Housing Administrations (FHA) minimum property standards. The process begins once an offer is accepted on a house, at which point the lender orders the appraisal from an FHA-approved appraiser. The appraiser conducts a thorough inspection of the property, both inside and out, to assess its condition and verify that it complies with FHA guidelines. This includes checking the structural integrity of the home, ensuring that it is safe and secure, and confirming that it meets basic health and safety requirements.
What happens if an FHA appraisal identifies required repairs?
If the FHA appraisal identifies issues that need to be addressed, the appraiser will list the necessary repairs in the appraisal report. These repairs must be completed before the loan can be approved and the property can close. Common issues might include problems with the roof, plumbing, electrical systems, or safety hazards like peeling lead-based paint. The lender will review the appraisal report, and the buyer and seller will need to negotiate who will be responsible for completing the repairs. In some cases, the seller may agree to make the repairs, or the buyer might take on the responsibility as a condition of the sale.
How does an FHA appraisal differ from a home inspection?
An FHA appraisal and a home inspection serve different purposes, although both involve evaluating the condition of the home. The FHA appraisal is primarily for the lenders benefit to ensure that the loan amount does not exceed the homes market value and that the property meets FHA’s minimum standards, a home inspection is comprehensive and conducted for the buyers benefit, providing a detailed analysis of the homes condition, including potential issues that might not affect the appraisal but could impact future maintenance and repairs.
What are FHA loan approval conditions?
FHA loan approval conditions involve several key criteria that must be met for your loan to be fully approved. First, your income and employment history will be closely reviewed to ensure that you have a stable and sufficient income to cover your mortgage payments. You will need to provide documentation recent pay stubs, W-2 forms, and tax returns to verify your income, your debt-to-income (DTI) ratio will be assessed, with most lenders requiring a DTI of no more than 43%, though higher ratios may be allowed with compensating factors like a stronger credit score.
What happens during FHA loan underwriting?
During the FHA loan underwriting process, the underwriter reviews all your financial documents and may issue a conditional approval, which means your loan is likely to be approved once you meet certain conditions. These conditions often include providing documentation, updated bank statements or letters explaining large deposits. The underwriter may also request verification of homeowners insurance or a gift letter if you are using gift funds for your down payment. Fulfilling these conditions promptly is crucial to keep the loan process on track.
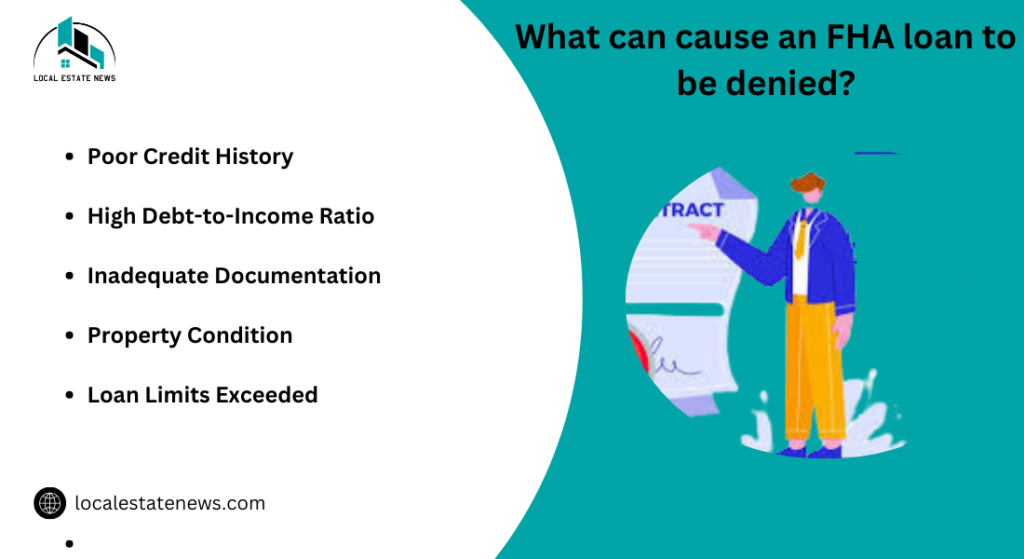
What can cause an FHA loan to be denied?
An FHA loan can be denied for several reasons, even after receiving conditional approval. Common reasons include the discovery of new debts that change your financial profile, failure to verify critical documents, or issues with the property itself, a low appraisal value or significant repair needs identified during the home inspection. It is important to avoid taking on new debt and to stay in close communication with your lender throughout the process to ensure all conditions are met and the loan can be finalized successfully.
What are the key takeaways from the FHA loan process?
Navigating the FHA loan process involves understanding several crucial aspects, from the initial approval conditions to the underwriting and final approval. The FHA loan program is designed to make homeownership accessible, particularly for first-time buyers and those with lower credit scores, it comes with specific requirements and conditions that must be met to secure the loan. These include verifying income, maintaining a manageable debt-to-income ratio, and ensuring the property meets FHA standards.
How can you ensure a smooth FHA loan approval process?
To ensure a smooth FHA loan approval process, it is essential to stay organized and responsive to your lenders requests. This includes promptly providing any additional documentation required during the underwriting phase and avoiding new debts that could alter your financial profile. Understanding the conditions that could lead to a loan denial, issues with the property appraisal or unverified documents, will help you navigate the process more effectively and increase your chances of a successful outcome.
How Should You Conclude Consideration of FHA Loans in Your Home Buying Process?
When concluding the evaluation of FHA loans in your home buying process, it is crucial to consider how this option aligns with your financial situation and homeownership goals. FHA loans offer unique benefits, lower down payment requirements and more lenient credit qualifications, which can make homeownership accessible for first-time buyers or those with less than perfect credit.
Here are some highlights to consider:
- Accessibility: FHA loans are especially beneficial for individuals who might not qualify for conventional financing due to lower credit scores or smaller down payments.
- Financial Planning: Incorporate FHA loans into your home buying checklist to ensure all financing options are considered and that you choose the best path to suit your financial health and homeownership objectives.
In conclusion, FHA loans can be a strategic component of your home buying checklist, offering a viable path to homeownership for those who benefit from more flexible lending standards. As you finalize your checklist, weigh the pros and cons of FHA loans within the context of your financial landscape to make an informed and strategic decision that will support your long-term goals. Remember, the right mortgage choice will provide not just a house, but a sustainable and affordable home.









